Power Outage Survival Kit: Stay Safe & Connected
Power outages: We’ve all been there. The lights flicker, then poof — everything goes dark. Millions of us experience this frustrating disruption every year across the US. This guide explores why power outages happen, which states are most affected, and how you can prepare. We'll cover creating an emergency kit, exploring backup power, and showcasing how KEUTEK's charging cables and portable power solutions can keep you connected when the grid goes down. Let's get you ready for anything.

Portable Solar Power Bank 26800mAh - 99Wh Fast Charger
Lithium Polymer (Li-Po) battery. PD fast charging. Holds up to 8 days of reliable power on a single charge. Boasts a charging speed 50% faster than ordinary portable chargers.
Shop NowThe Growing Threat of Power Outages
What is a Power Outage?
A power outage is the interruption of the electricity supply to a given area. This can range from a brief flicker of the lights to an extended blackout lasting days or even weeks. Power outages are a common occurrence, impacting millions of people across the United States every year. While short outages can be a minor inconvenience, longer-term power failures can disrupt daily life, impacting everything from refrigeration and cooking to communication and transportation. Preparing for power outages is key to weathering these events safely and comfortably.
Several factors can contribute to power outages. Severe weather events, such as hurricanes, thunderstorms, ice storms, and heat waves, are a leading cause. Natural disasters like wildfires and earthquakes can also damage electrical infrastructure, leading to widespread outages. Equipment failures, aging infrastructure, and human error also play a role. Even seemingly minor incidents like a vehicle hitting a power pole or an animal interfering with electrical equipment can cause localized outages.
The frequency and duration of power outages are increasing, making reliable backup power solutions more critical than ever. While the average outage might last a couple of hours, major events can extend for days or weeks, posing significant challenges. Investing in portable power solutions, like KEUTEK's fast-charging portable power banks, can provide essential power for devices during these extended outages, ensuring you stay connected and prepared. These portable power banks are designed for various situations, from everyday use to emergency preparedness.
Key Takeaways
- Power outages are increasingly common: Severe weather and aging infrastructure contribute to more frequent and longer-lasting outages, making personal preparedness essential.
- Portable power is a practical solution: Investing in portable power banks and power stations offers a reliable backup for essential devices during outages, keeping you connected and comfortable.
- Planning ahead minimizes disruption: Preparing for outages with emergency kits, communication plans, and backup power ensures you're ready to weather any power disruption, whether at home or at work.
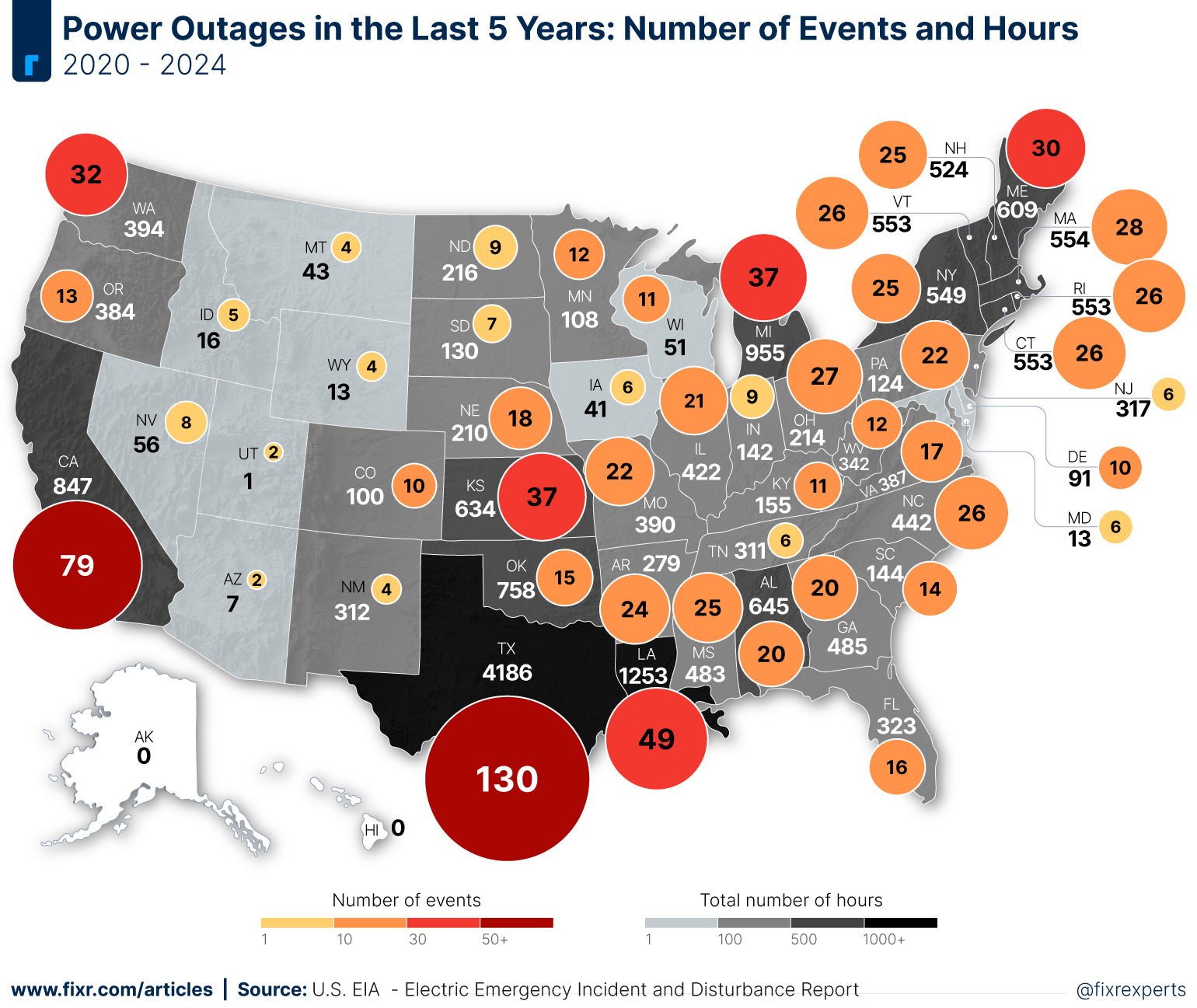
Power Outages by State: Frequency and Duration
Power outages can vary widely in both frequency and duration, depending on several factors including geographical location, local infrastructure, and susceptibility to natural disasters. States that are prone to severe weather conditions, such as hurricanes, tornadoes, and ice storms, tend to experience more frequent and prolonged outages.
Which States Have the Most Power Outages?
- Maine: Maine has the highest frequency of outages, mainly due to its rural power grid and frequent winter storms that cause significant damage to power infrastructure.
- Alaska: Harsh weather conditions, including extreme cold and snowstorms, combined with remote infrastructure, result in frequent outages in Alaska.
- Louisiana: Louisiana is heavily affected by hurricanes and tropical storms, causing widespread outages, especially during hurricane season.
Where are Power Outages the Longest?
- Louisiana: Due to the frequency of hurricanes and tropical storms, Louisiana residents often face long recovery times after outages.
- New York: Ice storms and snow blizzards often lead to prolonged power outages in this state, especially during the winter months.
- Maine: Due to the state's rural infrastructure and susceptibility to winter weather, outages can last for extended periods in Maine.
Regional and Seasonal Outage Trends
Power outages aren’t uniform across the country. Frequency and duration vary significantly depending on geographical location, the quality of local infrastructure, and susceptibility to natural disasters. States prone to severe weather, like hurricanes, tornadoes, and ice storms, tend to experience more frequent and prolonged outages. For example, Maine experiences frequent outages due to its rural power grid and vulnerability to winter storms. Similarly, Louisiana is significantly affected by hurricanes and tropical storms, leading to widespread outages, especially during hurricane season. Coastal regions, California, and the Midwest—all susceptible to various natural disasters—also experience more frequent and longer outages. Having a reliable car charger can be invaluable in these situations.
Impact of Infrastructure Quality on Outage Duration
The duration of an outage is directly related to the cause and the extent of damage to the electrical infrastructure. Most technical or minor outages in the U.S. last about one to two hours. However, outages caused by major natural disasters can last for days, even weeks, as we often see with hurricanes. The type of infrastructure plays a crucial role. Areas with robust infrastructure, such as underground cables, tend to experience shorter outages because they are less susceptible to weather damage. Investing in resilient infrastructure is key to minimizing disruption and ensuring faster recovery. A portable power solution can bridge the gap during these extended outages.
What Causes Power Outages?
The primary causes of power outages across the U.S. can be broken down into five main categories: natural disasters, aging infrastructure, human error, cyberattacks, and equipment failure.
1. Natural Disasters
Natural disasters such as hurricanes, tornadoes, floods, and wildfires are the leading cause of power outages in the U.S. In states like Florida, Texas, and California, extreme weather often results in mass outages. The increasing severity of these weather events, attributed to climate change, continues to place strain on the power grid.
2. Aging Infrastructure
Many states in the U.S. have outdated power grids that are unable to keep up with modern energy demands. For instance, California’s grid is often stressed by high temperatures and increased energy consumption, leading to rolling blackouts.
3. Outdated or Poorly Maintained Equipment
Outdated or poorly maintained equipment significantly contributes to power outages across the United States. Many states grapple with aging infrastructure struggling to meet modern energy consumption demands. California's power grid, for example, frequently faces stress during high temperatures, leading to rolling blackouts as the system fails to cope. This highlights the critical need for upgrades and maintenance to ensure reliable and efficient power delivery. Investing in smart grid technologies can improve grid resilience and responsiveness, minimizing the impact of equipment failures.
Furthermore, neglecting equipment maintenance allows small issues to escalate into widespread outages. Even minor faults can cascade into significant disruptions, affecting millions of residents and businesses. As electricity demand rises, investing in modernizing and maintaining power infrastructure becomes even more critical. Regular inspections and timely repairs are crucial for preventing outages and ensuring reliable electricity delivery. Resources like the North American Electric Reliability Corporation (NERC) offer valuable information and standards for maintaining grid stability.
For individuals, well-maintained personal electronics are equally important. Using reliable, up-to-date charging equipment, like KEUTEK’s fast wall chargers and portable power solutions, optimizes charging performance and contributes to device safety and longevity. Investing in quality equipment minimizes device failure risks and ensures power access, even during outages. Consider adding a portable power bank to your emergency kit for added peace of mind.
3. Human Error
Human error, including operational mistakes or accidents, contributes to a smaller percentage of outages but can still be significant. Examples include accidental damage to power lines during construction projects or improper maintenance of substations.
4. Vandalism
Vandalism and targeted attacks on power infrastructure are a growing concern. In December 2022, a North Carolina community suffered the impact of utilities vandalism, with around 40,000 customers losing power after two power substations were damaged. These attacks, while not as frequent as natural disasters, can cause significant disruption and highlight the vulnerability of the power grid. Targeted attacks on substations and other critical infrastructure can lead to widespread outages, impacting essential services and daily life.
In 2022 alone, the U.S. electrical grid experienced at least 103 physical and cyberattacks, the highest number in a decade. While not all of these attacks resulted in power outages, they underscore the increasing need for enhanced security measures to protect the nation's power infrastructure. The vulnerability of our energy infrastructure is a serious concern, and bolstering energy security and resilience is crucial to mitigating these threats.
4. Cyberattacks
As digital infrastructure becomes more integrated into power grids, cyberattacks pose a growing threat. Although rare, such attacks could result in prolonged outages if key components of the grid are compromised.
5. Equipment Failure
Wear and tear on critical components such as transformers, substations, and power lines can lead to equipment failure. Without timely upgrades, this failure can trigger widespread outages, especially during peak demand seasons.

300W Portable Power Station LiFePO4 (296Wh/600W Peak)
Ideal for emergencies. Powers small appliances like CPAPs, air pumps, TVs, fans, and mini fridges. Supports up to nine devices simultaneously.
Shop NowPower Outage Trends Across the U.S.
West Coast Power Outages
The West Coast, particularly California, is extremely vulnerable to power outages. Due to frequent wildfires, many electric utilities, including Pacific Gas & Electric (PG&E), have implemented Public Safety Power Shutoffs (PSPS) as a preventative measure. This strategy has been used to prevent fires from starting due to downed or damaged power lines.
Northeast Power Outages
In the Northeast, New York, New Jersey, and Massachusetts frequently experience power outages due to harsh winter weather. Ice storms can weigh down power lines, leading to breaks and outages that can last days or even weeks in remote areas.
South and Southeast Power Outages
The Southeast region, particularly Florida and Louisiana, is prone to hurricanes, making power outages during storm season almost inevitable. Utilities in this region are gradually strengthening their grid infrastructure, but much work remains to protect residents from prolonged outages.
Midwest Power Outages
The Midwest states like Michigan, Illinois, and Ohio frequently experience outages caused by thunderstorms and tornadoes. The wide, flat landscape of this region allows for severe storm systems to wreak havoc on power lines.
The Economic Impact of Power Outages
Power outages carry significant economic consequences. Businesses experience revenue losses, while individuals often face additional costs for temporary solutions like generators or alternative accommodation. For critical industries like healthcare, outages can disrupt operations and place lives at risk. On a national scale, power outages contribute to billions of dollars in lost productivity annually.
Power Outages: Impacts by Industry
- Manufacturing: Delays in production due to power outages can lead to missed deadlines and financial losses.
- Healthcare: Hospitals are often forced to rely on backup generators, but even minor power interruptions can impact patient care.
- Retail: Stores without power are unable to process transactions, leading to lost sales.
Preparing for a Power Outage
Power Outage Preparedness for Individuals
- Invest in Backup Power: Homeowners can purchase backup generators to power essential devices during an outage.
- Create an Emergency Kit: Stock up on batteries, non-perishable food, and water in case of extended outages.
- Prepare for Communication: Keep your phone fully charged, and invest in a backup battery pack to ensure communication during emergencies.
Storing Water for Emergencies
Access to clean water is crucial during emergencies. A simple yet effective way to prepare is by filling your bathtub before a predicted storm. This provides a readily available reserve of water for various needs if your regular supply gets disrupted or contaminated. Think of it as a large, built-in emergency water tank. While a bathtub provides a good amount of water, consider supplementing it with additional storage methods like clean, food-grade containers. Aim for at least one gallon of water per person per day to cover drinking, cooking, and basic hygiene for a minimum of three days. And don't forget your furry friends! Factor your pets into your water storage calculations.
Using Stored Water During an Outage
Stored water becomes invaluable during a power outage. While bathtub water isn’t ideal for drinking directly, you can purify it using water purification tablets or by boiling it for at least one minute. This purified water is then safe for drinking. You can also use your stored water for other essential tasks like washing dishes, sponge baths, and flushing toilets. If you have a portable power station, you can even power a small water filter for easier purification.
Grid Protection Measures and Consumer Preparedness
Power companies use various strategies to protect the grid and minimize outages. These include high-voltage fuses that trip during power surges, preventing further damage, and lightning rods that redirect lightning strikes away from critical infrastructure. Some utilities also use real-time monitoring to anticipate peak usage and adjust output accordingly. Preparing for outages on a personal level is also essential. Consider investing in a portable power station or generator for backup power. A gas stove or wood-burning fireplace can provide alternative heating. Don't forget essential supplies like flashlights, a battery-powered radio, and backup charging options for your phone. A solar-powered charger can be incredibly useful when the grid is down.
Power Outage Preparedness for Businesses
- Install Backup Generators: Ensure your business can operate during outages by installing reliable backup generators.
- Develop a Continuity Plan: Create a plan for how your business will operate during and after power outages, focusing on critical systems and data protection.
- Collaborate With Utility Companies: Build relationships with local utility providers to ensure your business is prioritized during power restoration efforts.
Real-Time Outage Tracking and Reporting
Staying informed during a power outage is crucial for both safety and planning. Thankfully, several resources offer real-time outage tracking and reporting, helping you understand the scope of the outage and anticipate restoration times. Knowing where to find information empowers you to make informed decisions and minimize disruption.
Real-Time Outage Tracking Resources
Several websites and apps provide up-to-the-minute information on power outages across the US. PowerOutage.us is a particularly helpful website that tracks outages nationwide, with data updated approximately every ten minutes. This resource allows you to quickly assess the extent of an outage and see which areas are affected. For a more localized view, especially for those in Virginia, UticaOD offers real-time outage information for Charlottesville and the rest of the US, gathering data from over 1,000 utility companies and refreshing every 15 minutes. Using these tools can give you a clearer picture of the situation and help you estimate when power might be restored.
Reporting Outages and Accessing Information from Your Energy Provider
Your local energy provider is your primary point of contact for reporting outages and accessing specific information about restoration efforts. Dominion Energy, for instance, offers multiple ways to report outages through their website and mobile app. The app also provides convenient features for managing your account and monitoring energy usage, making it a valuable tool even when the power is on. In emergencies involving downed power lines, immediately contact Dominion Energy at 1-866-366-4357. Remember, safety is paramount—never approach downed power lines; maintain a safe distance of at least 30 feet. Dominion Energy's real-time outage map on their website displays affected areas and estimated restoration times, which can be invaluable for planning during an outage.
How Utilities Are Tackling Power Outages
To combat the increasing frequency of outages, utility companies are investing in grid modernization projects. These efforts include:
- Smart Grid Technology: Implementing smart grids allows utility companies to monitor and control the flow of electricity more effectively, preventing overloads and reducing the time needed to restore power after an outage.
- Underground Power Lines: In some regions, power lines are being buried underground to protect them from storm damage. This is particularly relevant in hurricane-prone states like Florida.
- Microgrids: Microgrids provide localized power generation and distribution, reducing the reliance on large, centralized grids and decreasing the risk of widespread outages.
The Future of Power Grid Resilience
As climate change continues to increase the frequency of extreme weather events, the U.S. power grid must evolve to become more resilient. Investment in renewable energy sources, smart grid technology, and proactive maintenance will be essential in reducing the economic and social impact of power outages.
What Can We Do About Power Outages?
- Upgrade Infrastructure: Continuous investment in power grid infrastructure is critical to reducing outage frequency.
- Focus on Sustainability: Renewable energy sources such as solar and wind can help to decentralize the grid and make it more resilient.
- Adopt Smart Technology: Integrating smart meters and grid management systems will allow utilities to pinpoint outages more quickly and restore service faster.

Portable Solar Power Bank 26800mAh - 99Wh Fast Charger
Lithium Polymer (Li-Po) battery. PD fast charging. Holds up to 8 days of reliable power on a single charge. Boasts a charging speed 50% faster than ordinary portable chargers.
Shop NowUnderstanding Power Outages
Power outages remain a significant issue across the United States, affecting millions of people annually. These outages can be caused by a variety of factors, but states like Maine, Alaska, and Louisiana are particularly vulnerable due to frequent natural disasters like winter storms, hurricanes, and other severe weather events.
The economic and social impacts of these outages are considerable. Businesses, especially those in critical industries like healthcare and manufacturing, suffer from lost productivity and potential operational hazards. Individuals face additional costs for temporary solutions like generators, and prolonged outages can disrupt daily life significantly.
To mitigate the effects of power outages, preparation is essential. This includes investing in backup power solutions, such as portable power stations or generators, and creating emergency kits with food, water, and other essential supplies. Additionally, adopting smart technologies, such as smart meters and grid management systems, helps utilities respond more efficiently to outages and prevent further disruptions.
Utility companies are taking steps to address these challenges by modernizing the aging power grid, incorporating renewable energy sources like solar and wind, and utilizing microgrids to decentralize power distribution. These efforts aim to make the grid more resilient and reduce the frequency and duration of outages in the future.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Causes Power Outages?
Power outages in the U.S. are primarily caused by extreme weather events such as hurricanes, tornadoes, and ice storms. Other factors include aging infrastructure, human error, cyberattacks, and equipment failures.
Which States Experience the Most Power Outages?
The states with the highest frequency of power outages include Maine, Alaska, and Louisiana. These states are particularly affected by natural disasters like winter storms and hurricanes, which frequently disrupt their power grids.
How Can I Prepare for a Power Outage?
Individuals can prepare for power outages by investing in backup generators or portable power stations, creating an emergency kit with essentials like food, water, and batteries, and ensuring their communication devices are fully charged or have backup power sources.
How Long Do Power Outages Typically Last?
Power outages can vary in duration. States like Louisiana and New York, which are frequently hit by hurricanes and winter storms, can experience outages lasting several days or even weeks. Rural areas may face longer recovery times compared to urban centers.
How Can Businesses Prepare for Power Outages?
Businesses can mitigate the effects of power outages by installing backup generators, developing a continuity plan for operations during outages, and collaborating with utility providers to prioritize power restoration. Investing in uninterruptible power supply (UPS) systems can also help protect critical systems from sudden disruptions.
















Leave a comment